Scatterings
Tiny Room-Temperature Plasmon Lasers
Researchers demonstrated a nanoscale plasmon laser that works at room temperature, in air.
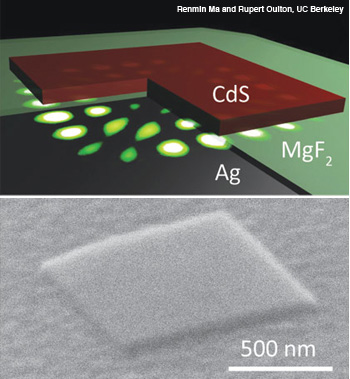 (Top) Schematic of a plasmon laser showing a cadmium sulfide square atop a silver (Ag) substrate separated by a 5-nm gap of magnesium fluoride. (Bottom) Electron microscope image of the plasmon laser.
(Top) Schematic of a plasmon laser showing a cadmium sulfide square atop a silver (Ag) substrate separated by a 5-nm gap of magnesium fluoride. (Bottom) Electron microscope image of the plasmon laser.
A nanoscale plasmon laser that works at room temperature, in air, was recently demonstrated by researchers in Xiang Zhang’s group at the University of California, Berkeley. In a tiny lasing cavity, the coherent plasmons travels in a tight gap of 5 nm in a smaller mode area than the best diffraction-limited spot from a conventional, focused laser beam (Nature Materials, doi: 10.1038/nmat2919). Previous semiconductor plasmon lasers had difficulty confining the light and operated at cryogenic temperatures in vacuum to reduce losses.
…Log in or become a member to view the full text of this article.
This article may be available for purchase via the search at Optica Publishing Group.
Optica Members get the full text of Optics & Photonics News, plus a variety of other member benefits.
