Scatterings
3-D Self-Assembling Point-Source Microlasers
Tiny spherical drops in liquid self-organize into lasing cavities that demonstrate low threshold, emit in all directions, and can be designed with wavelengths from ultraviolet to infrared.
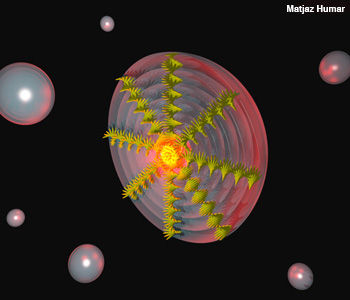 A cut-away view of a microlaser droplet. The reddish center represents lasing dye molecules, while the radial yellowish helices indicate cholesteric liquid crystal molecules.
A cut-away view of a microlaser droplet. The reddish center represents lasing dye molecules, while the radial yellowish helices indicate cholesteric liquid crystal molecules.
Tiny spherical drops in liquid self-organize into lasing cavities that demonstrate low threshold, emit in all directions, and can be designed with wavelengths from ultraviolet to infrared. These lasers are made of droplets of dye-doped cholesteric liquid crystals (CLCs) suspended in a carrier fluid (Opt. Express 18, 26995), and they are part of a long-term project on soft-matter photonic devices carried out in Igor Musevic's lab at the J. Stefan Institute and University of Ljubljana, Slovenia.
…Log in or become a member to view the full text of this article.
This article may be available for purchase via the search at Optica Publishing Group.
Optica Members get the full text of Optics & Photonics News, plus a variety of other member benefits.
